- Details
- Hits: 1428
On the NMRCM-2012 conference that took place in St. Petersburg on the 9-14 of July 2012 were presented two talks
P. Tolstoy, B. Koeppe, S. Pylaeva, E. T. J. Nibbering, D. Sebastiani, G. Denisov, H.-H. Limbach, “Solvation of H-Bonded Complexes by Polar Aprotic Solvents: Coupling of the Proton Position to the Solvent Configuration”.
and
S. Pylaeva, P. Tolstoy, B. Koeppe, C. Allolio, D. Sebastiani, G. Denisov, “Fluctuations of H-bond geometry due to the solvent-solute interactions studied by means of computer simulations”.
The latter was awarded for the best poster.
- Details
- Hits: 1528
J. Guo, P. M. Tolstoy, B. Koeppe, N. S. Golubev, G. S. Denisov, S. N. Smirnov, H.-H. Limbach
«Hydrogen Bond Geometries and Proton Tautomerism of Homo-Conjugated Anions of Carboxylic Acids Studied via H/D Isotope Effects on 13C NMR Chemical Shifts»
J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, ASAP.
DOI: 10.1021/jp304943h.

Abstract:
Ten formally symmetric anionic OHO hydrogen bonded complexes, modeling Asp/Glu amino acid side chain interactions in nonaqueous environment (CDF3/CDF2Cl solution, 200–110 K) have been studied by 1H, 2H, and 13C NMR spectroscopy, i.e. intermolecularly H-bonded homoconjugated anions of acetic, chloroacetic, dichloroacetic, trifluoroacetic, trimethylacetic, and isobutyric acids, and intramolecularly H-bonded hydrogen succinate, hydrogen rac-dimethylsuccinate, hydrogen maleate, and hydrogen phthalate. In particular, primary H/D isotope effects on the hydrogen bond proton signals as well as secondary H/D isotope effects on the 13C signals of the carboxylic groups are reported and analyzed. We demonstrate that in most of the studied systems there is a degenerate proton tautomerism between O-H···O– and O–···H–O structures which is fast in the NMR time scale. The stronger is the proton donating ability of the acid, the shorter and more symmetric are the H-bonds in each tautomer of the homoconjugate. For the maleate and phthalate anions exhibiting intramolecular hydrogen bonds, evidence for symmetric single well potentials is obtained. We propose a correlation between H/D isotope effects on carboxylic carbon chemical shifts and the proton transfer coordinate, q1 =1/2(rOH – rHO), which allows us to estimate the desired OHO hydrogen bond geometries from the observed 13C NMR parameters, taking into account the degenerate proton tautomerism.
- Details
- Hits: 1583
Gurinov, A. A.; Mauder, D.; Akcakayiran, D.; Findenegg, G. H.; Shenderovich, I. G.
«Does Water Affect the Acidity of Surfaces? The Proton-Donating Ability of Silanol and Carboxylic Acid Groups at Mesoporous Silica.»
ChemPhysChem 2012, 13 (9), 2282-2285.
DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201200204
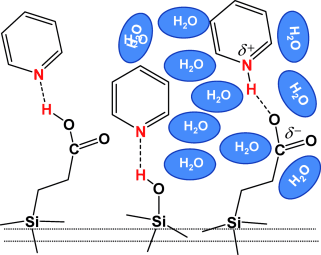
Solvation at the interphase:
A study of the influence of water on the effective acidity of silanol and carboxylic acid groups of propionic acid functionalized SBA-15 reveals that to affect the proton-donating ability of an acidic group at the surface, water should be able to form a solvation shell around that group. As a result, water does not affect the acidity of native SBA-15 but dramatically enhances that of SBA-15 functionalized with propionic acid moieties.
- Details
- Hits: 1620
Key themes at Conference:
• Gateway into Finnish Innovation systems
• Experience how to build up an effective open innovation space.
• Training in technology transfer, entrepreneurship and research infrastructure management
• Networking possibility to meet Finnish experts.
- Details
- Hits: 1558
Gorobets, N. Y.; Yermolayev, S. A.; Gurley, T.; Gurinov, A. A.; Tolstoy, P. M.; Shenderovich, I. G.; Leadbeater, N. E.
«Difference between 1H NMR signals of primary amide protons as a simple spectral index of the amide intramolecular hydrogen bond strength.»
J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2011, 25 (4), 287-295.
DOI: 10.1002/poc.1910

Abstract
The effect of the intramolecular H-bonding of the primary amide group on the spectral properties and reactivity of this group towards electrophiles has been studied in systematic rows of 1,2,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-7,7-dimethyl-2,5-dioxo-1-R-quinoline-3-carboxamides and 2-aryliminocoumarin-3-carboxamides using 1H and 15N NMR spectroscopy and the kinetics of model reactions. The upfield signal of the amide proton that is not intramolecularly H-bonded (Ha) depends on external factors such as solvent nature and concentration. At the same time, the downfield chemical shift of the Hb proton (bonded by the intramolecular hydrogen bond) depends mostly on the strength of the intramolecular H-bond, which is affected by such internal factor as electron nature of substituent R. The substituent’s influence on the Hb proton’s chemical shift is more effective in deuterochloroform medium than in DMSO-d6 where the intramolecular hydrogen bond is less stable. The value Δδ(H) = δ(Hb) − δ(Ha) is suggested as a simple comparative spectral index of the intramolecular hydrogen bond strength in these and similar compounds. By contrast, the effect of R on the H15N NMR chemical shift of the amide nitrogen has turned out to be too small to estimate changes of the electron density at the nitrogen. The effect of the intramolecular H-bond on the reactivity of the amide group is twofold. When the cleavage of the H-bond occurs on the rate limiting step it dramatically reduces the reaction rate. In the other case, the strengthening of the H-bond favors the reaction rate because of the increase of the electron density at the amide nitrogen.




