Particle motion under an applied electric field is known as electrophoresis. The method used by SZ100 is known as laser Doppler electrophoresis. Sample particles are suspended in a solvent af known refractibe index n, velocity η and dielectric constant ε. The sample is irradiated with laser light of wavelength λ. An electric field with strength E is applied. Due to the electric field, the particles are moving. Since the particles are moving, the scattered light at angle ϑ is measured and the particle velocity V is determined from the frequency shift. Mobility is then readily obtained as the radio of velocity to electric field strength V/E. Zeta potential is then found mobility using a model, the most common of which is the Smulochowski model.
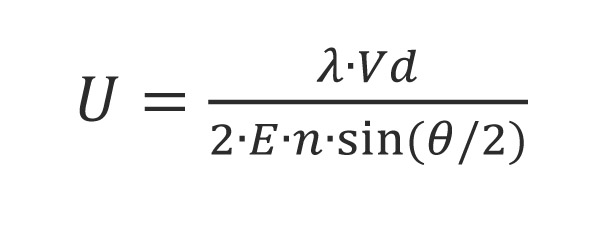
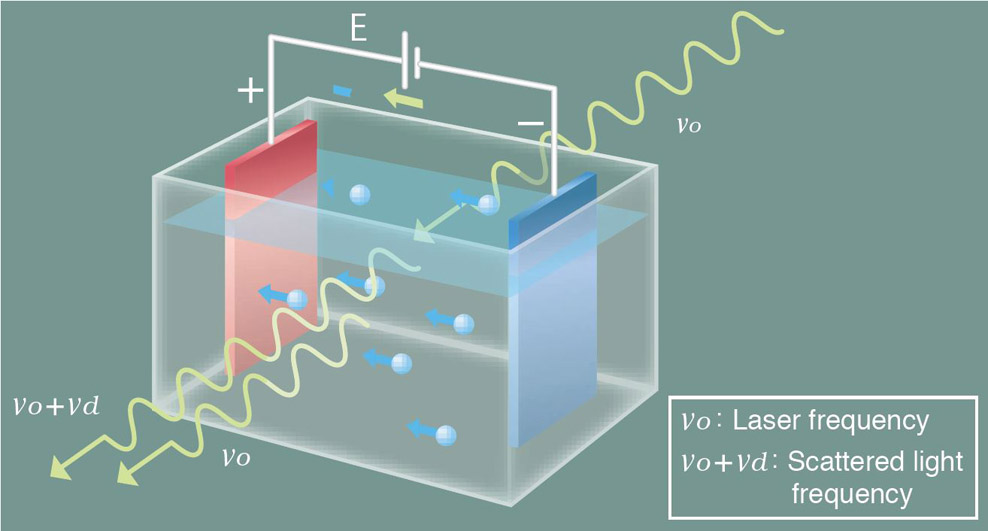
The following equation is used for the relationship between the calculated electrical mobility and zeta potential.

where ζ – Zeta potential, U – Electrical mobility, E – Electric field strength, ε – Solvent dielectric constant, n – Solvent refraction index, η – Solvent viscosity, f(ka) – henry coefficient
Overviews and methods
Under construction
Equipment
Laser particle analyzer SZ100
Contacts
The Leading Researcher in optical systems Alexandr Shimko
Specialist in spectroscopy and granulometry Anastasia Povolotckaia
Specialist in optical systems Alexandra Mikhaylova



