Journal of Luminescence Volume 192, December 2017, Pages 40-46
I.E. Kolesnikov, A.A. Kalinichev, M.A. Kurochkin, D.V. Mamonova, E.Yu. Kolesnikov, A.V. Kurochkin, E. Lähderanta, M.D. Mikhailov
New strategy for thermal sensitivity enhancement of Nd3+-based ratiometric luminescence thermometers
Journal of Luminescence Volume 192, December 2017, Pages 40-46
DOI: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.06.024
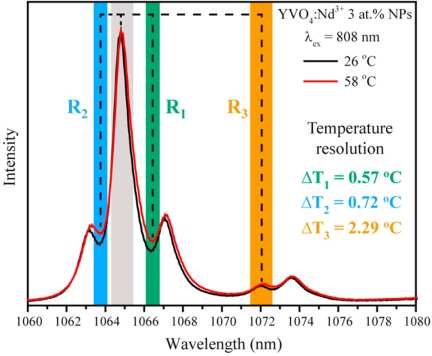
Accurate luminescence thermal sensing using nanophosphors that operate within biological windows is of great interest in bio- and nanomedicine. Here, we show that Nd3+-doped YVO4 NPs can act as nanothermometers in the second biological window upon 808 nm excitation. Significant enhancement of thermal sensitivity andtemperature resolution was achieved by optimal choice of wavelengths for ratiometric thermal calibration. It was concluded that thermal calibration should be calculated using integral intensities. The obtained temperature uncertainty together with the emission and excitation lying in the biological windows open the venue to the possible application of Nd3+-doped YVO4 NPs for real time sub-tissue luminescence thermal sensing with a subdegree resolution.
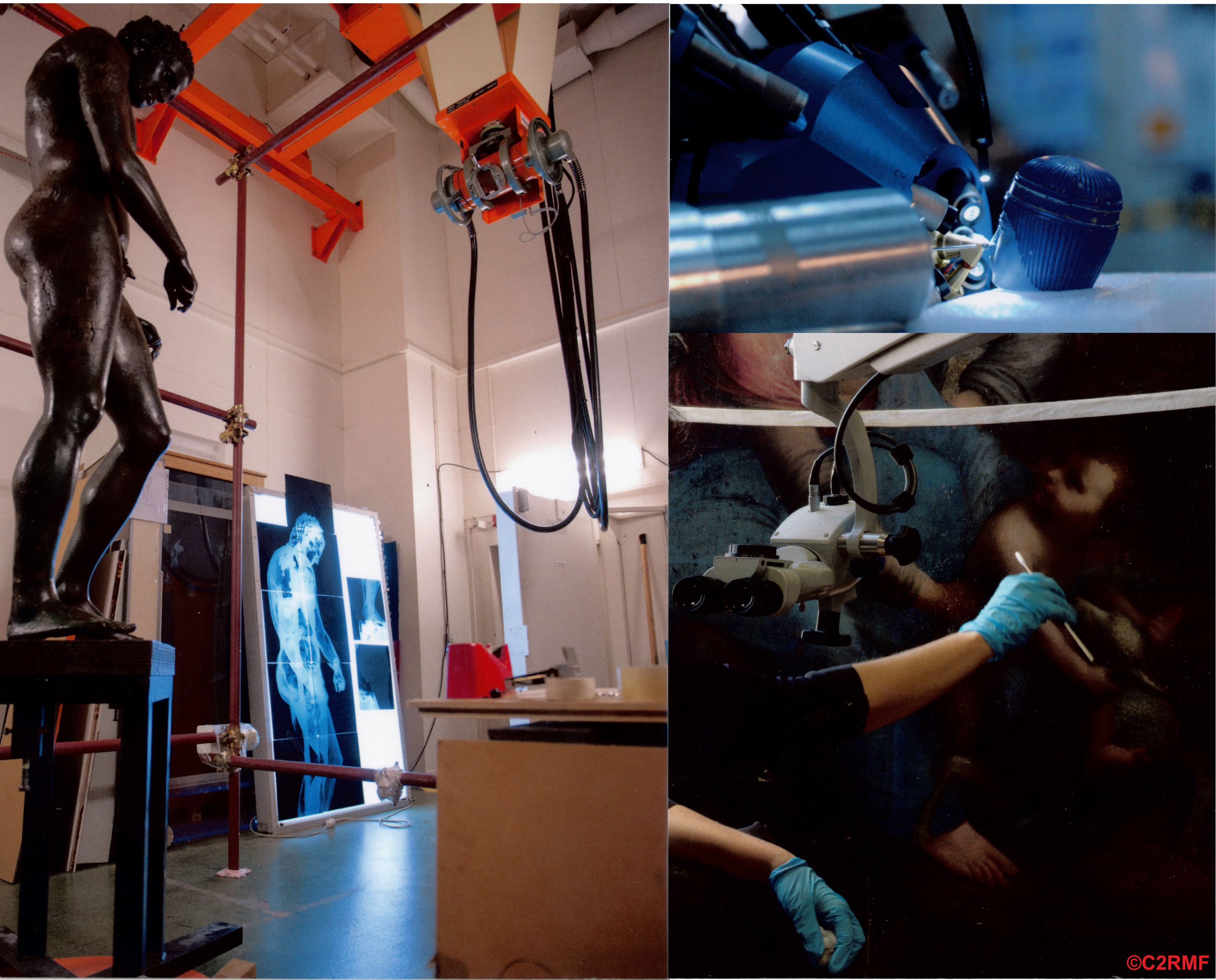
Vice-director of OLMR Dr. Anastasia Povolotckaia and Raman researcher Dmitrii Pankin at the beginning of December had visited the Center for the Restoration and Conservation of the Museums of France (Centre de Recherche et de Restavration des Musées de France (C2RMF) http://en.c2rmf.fr/).

Journal of Molecular Structure Volume 1149, December 2017, Pages 323-331
Anton Nikolaev, Ilya Kolesnikov, Olga Frank-Kamenetskaya, Maria Kuzmina
Europium concentration effect on сhаracteristics and luminescent properties of hydroxyapatite nanocrystalline powders
Journal of Molecular Structure Volume 1149, December 2017, Pages 323-331
DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.08.005
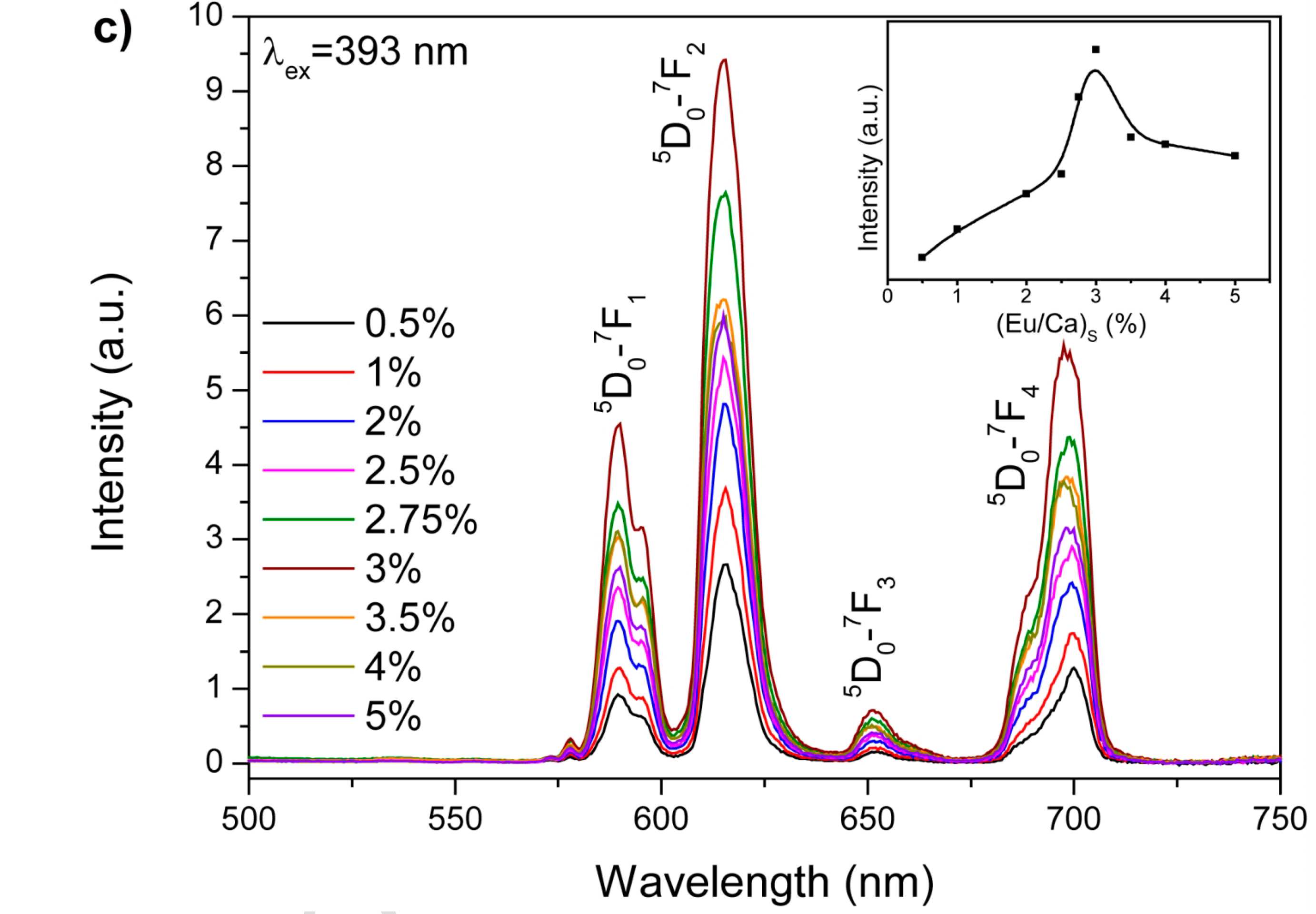
Series of Eu-apatites were synthesized by precipitation from aqueous solutions with the Eu/Ca atomic ratio from 0.5% to 5% at T = 90 ˚C. Resulting precipitates were studied using different experimental techniques including X-ray powder diffraction, infrared and raman spectroscopy, scanning elecrton microscopy, EDX and photoluminescent spectroscopy. Eu-doped Ca-deficit nanosized non-stoichiometric hydroxyapatite with high water content has been obtained throughout the experiment. Europium content in the synthesized apatites reaches 0.24 apfu (Eu/Ca = 2.5%). Relations between Eu content is the solution and precipitate have been established. It was shown that Eu-monacite starts to precipitate as secondary phase at Eu/Ca ratio in starting solution 1% or higher. Maximum luminescence is observed in apatite with ~2% Eu/Ca ratio (which equals to ~0.2 apfu and corresponds to 3% Eu/Ca ratio in the starting solution). As an important and brand-new result, apatite with 2% Eu/Ca ratio can be considered as the most appropriate material for the producing biolabels for luminescent research in medicine and biology.
The seminar was conducted in the framework of the International Scientific and Practical Conference "Heritage, Science and Technology"
Dr. Pascal Lievaux, France. Head of the Research and Scientific Policy Pilot department at the General Direction for Heritage, French Ministry of Culture.
Michel Menu, Head of the department of Research, Centre de recherche et de restauration des musées de France (C2RMF), Paris, France.
Tatiana Laska, Senior lecturer of the Faculty of Arts SPbSU
Nicolai Kurganov, Senior lecturer of the Faculty of Arts SPbSU

"Spectral-kinetic studies of photophysical processes involving dye molecules and biomolecules in the presence of noble metal nanoparticles"
Author - Andrei Yuryevich Zyubin, Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University.
The seminar was attended by specialists of the resource center, scientific and pedagogical workers of the Institute of Chemistry and Medical Faculty of St. Petersburg State University.


