- Информация о материале
- Просмотров: 2496
Journal of Molecular Structure Volume 1149, December 2017, Pages 323-331
Anton Nikolaev, Ilya Kolesnikov, Olga Frank-Kamenetskaya, Maria Kuzmina
Europium concentration effect on сhаracteristics and luminescent properties of hydroxyapatite nanocrystalline powders
Journal of Molecular Structure Volume 1149, December 2017, Pages 323-331
DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.08.005
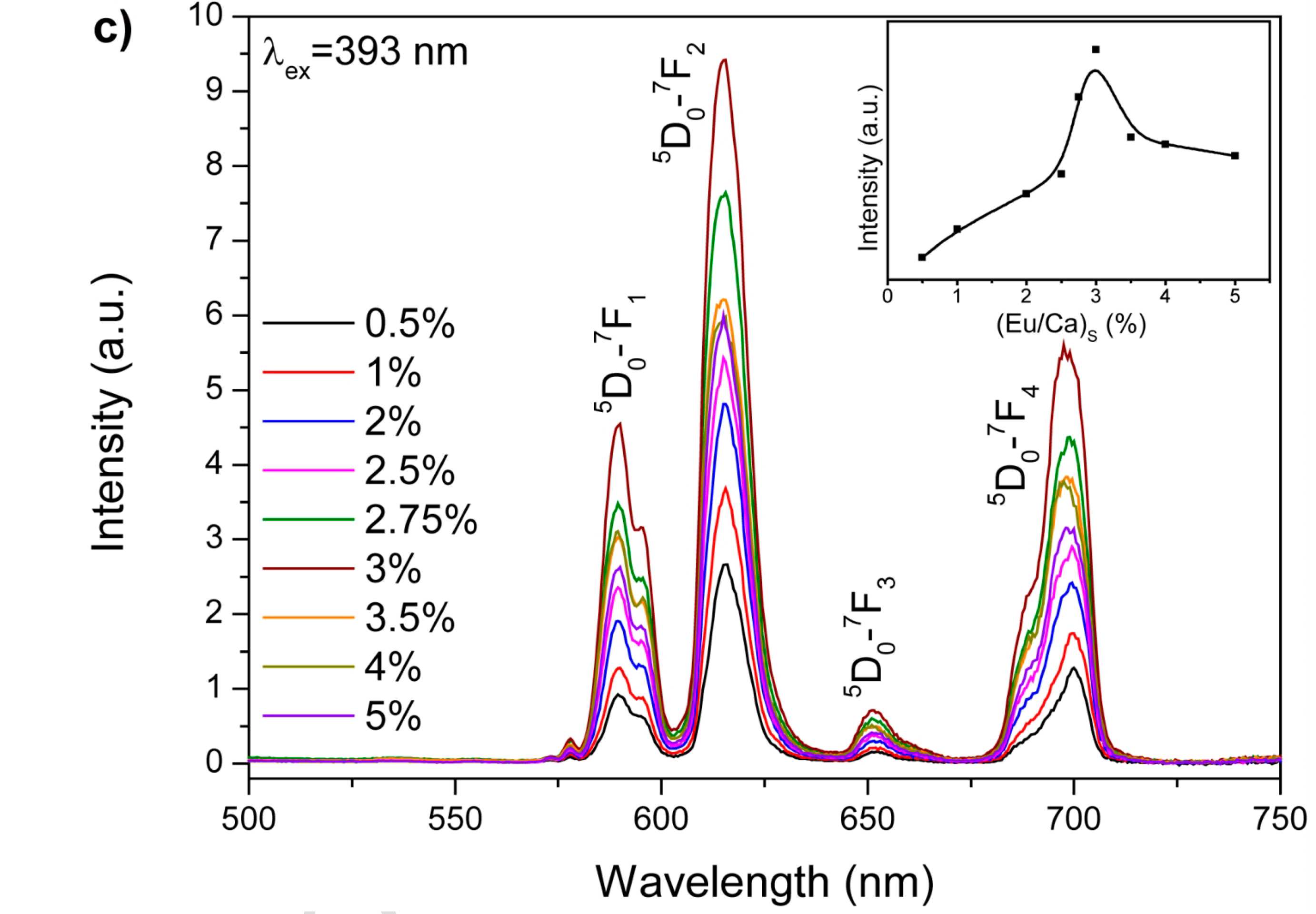
Series of Eu-apatites were synthesized by precipitation from aqueous solutions with the Eu/Ca atomic ratio from 0.5% to 5% at T = 90 ˚C. Resulting precipitates were studied using different experimental techniques including X-ray powder diffraction, infrared and raman spectroscopy, scanning elecrton microscopy, EDX and photoluminescent spectroscopy. Eu-doped Ca-deficit nanosized non-stoichiometric hydroxyapatite with high water content has been obtained throughout the experiment. Europium content in the synthesized apatites reaches 0.24 apfu (Eu/Ca = 2.5%). Relations between Eu content is the solution and precipitate have been established. It was shown that Eu-monacite starts to precipitate as secondary phase at Eu/Ca ratio in starting solution 1% or higher. Maximum luminescence is observed in apatite with ~2% Eu/Ca ratio (which equals to ~0.2 apfu and corresponds to 3% Eu/Ca ratio in the starting solution). As an important and brand-new result, apatite with 2% Eu/Ca ratio can be considered as the most appropriate material for the producing biolabels for luminescent research in medicine and biology.
- Информация о материале
- Просмотров: 2321
Семинар был проведен в рамках Международной научно-практической конференции АУИПИК – СПбГУ: «Наследие, наука и технологии»
В числе участников семинара:
Паскаль Лево (Pascal Liévaux) руководитель Департамента управления исследования и научной политики Генеральной Дирекции наследия Министерства культуры Франции
Мишель Меню (Michel Menu), директор Департамента исследований Лаборатории C2RMF Министерства культуры Франции, Париж
Ласка Татьяна Владимировна, старший преподаватель кафедры изобразительного искусства СПбГУ
Курганов Николай Сергеевич, старший преподаватель кафедры реставрации СПбГУ.

- Информация о материале
- Просмотров: 1980
ОПТИКА И СПЕКТРОСКОПИЯ, 2017, том 123, № 6, с. 124–129
О. И. Петрова, Д. В. Панькин, А. В. Поволоцкая, Е. В. Борисов, М. О. Безносова, Т. А. Кривулько, А. В. Курочкин
«Идентификация пигментов в красочных слоях объекта живописи по данным спектроскопии комбинационного рассеяния света»
ОПТИКА И СПЕКТРОСКОПИЯ, 2017, том 123, № 6, с. 124–129
DOI: 10.7868/S0030403417120133
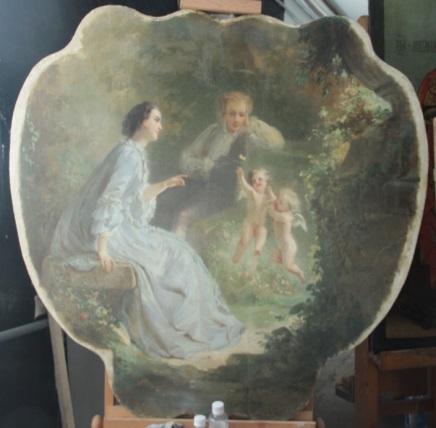



Методом спектроскопии комбинационного рассеяния света исследован пигментный состав и установлена техника написания авторского слоя в картине XIX века – предположительно десюдепорт работы Антуана Жана–Этьена Фэвра. Установлено использование автором следующих пигментов: киноварь и красители на основе гетита и гематита (для красных, желто-оранжевых и коричневых оттенков), ультрамарина и берлинской лазури (для синих оттенков), швейнфуртской зеленой и смеси синих и желтых оттенков (для получения зеленого цвета). Определено, что в качестве грунта применялись свинцовые белила.
- Информация о материале
- Просмотров: 2417
27 октября 2017 г в РЦ ОЛМИВ состоялся семинар на тему:
"Спектрально-кинетические исследования фотофизических процессов с участием молекул красителей и биомолекул в присутствии наночастиц благородных металлов"
Автор - Андрей Юрьевич Зюбин, Балтийский федеральный университет им. И.Канта.
На семинаре присутствовали специалисты ресурсного центра, научно-педагогические работники института химии и медицинского факультета СПбГУ.

- Информация о материале
- Просмотров: 2128
26 октября, четверг, 11:00 в РЦ ОЛМИВ состоится семинар от Компании «Специальные Системы. Фотоника» на тему: «Лазеры и приборы для анализа параметров лазерного излучения». Приглашаются все желающие.





