REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE Volume 47, No. 1, Pages 71-77
O.Yu. Kurapova, V.G. Konakov, A.S. Grashchenko, N.N. Novik, S.N. Golubev and I.A. Ovid’ko
NANOTWINNED COPPER-GRAPHENE COMPOSITES WITH HIGH HARDNESS
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE Volume 47, No. 1, Pages 71-77
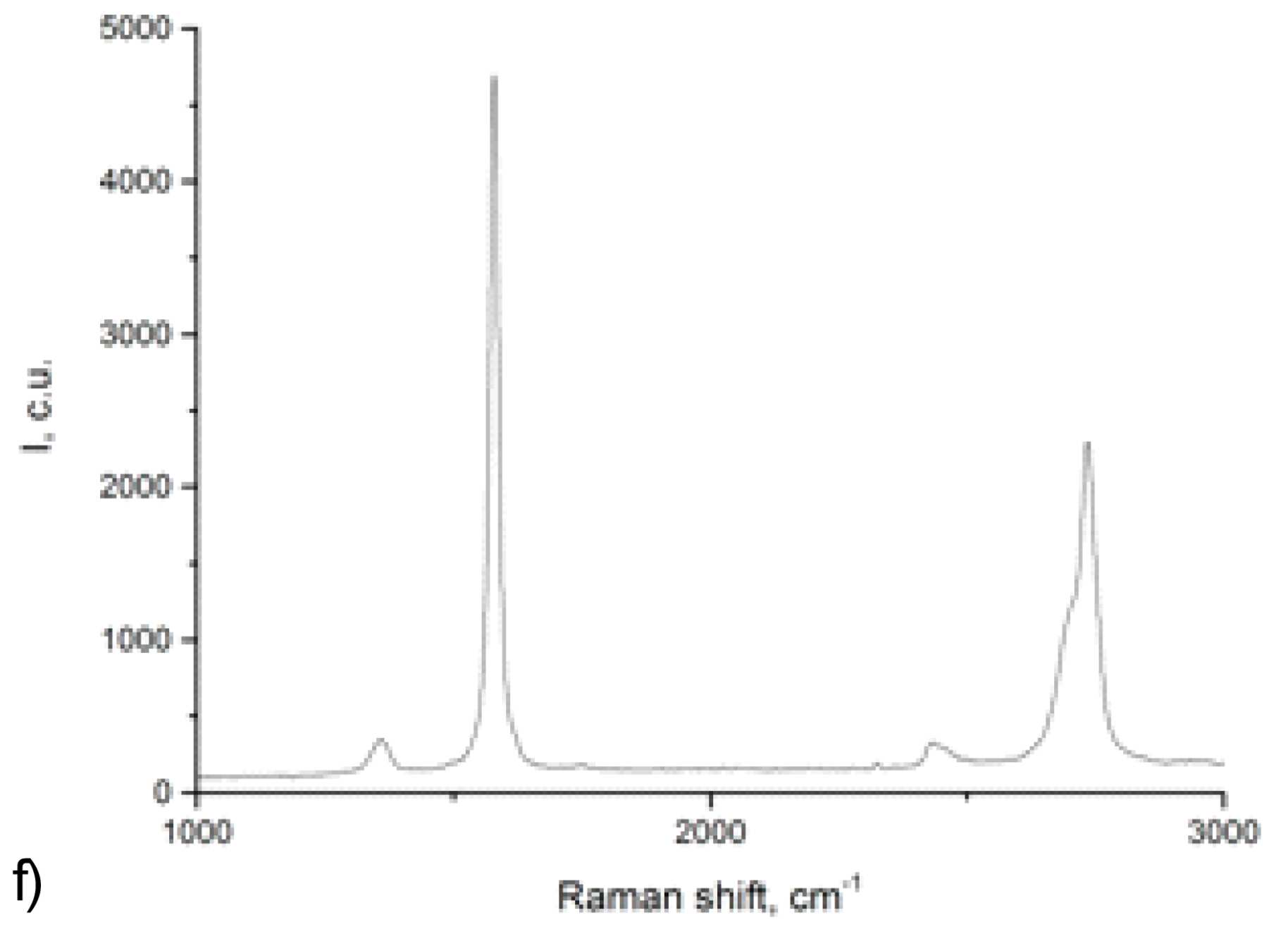
This paper addresses fabrication, structure, and hardness characteristics of nanotwinned (ntw) copper-graphene composites. The composites were fabricated by electrodeposition from 1M CuSO4·6H2O mixed water-alcohol solution containing graphene-graphite mixture stabilized by non-ionic surfactant. We fabricated two-layer solids each consisting of ntw copper layer and ntw copper-graphene layer. The synthesized two-layer specimens were examined in nanoindentation tests and showed high hardness values up to 3 GPa. The maximum hardness value of 3 GPa is higher than those of pure ntw copper and copper-graphene composites, taken from the literature.
29.03.17 Начат телефонный опрос по теме "Социальные практики питания петербуржцев". Квотная выборка не менее 1000 респондентов, жителей Санкт-Петербурга. Научный руководитель проекта Юрий Витальевич Веселов, доктор социологических наук, профессор кафедры экономической социологии.
28.03.17 Завершен телефонный опрос по теме "Устойчивость населения к социальным рискам". Объем выборки - 1000 респондентов, жителей Санкт-Петербурга. Приступили к обработке данных.
Dalton Transactions Issue 12, Pages 3895-3905
Anastasia I. Solomatina, Irina O. Aleksandrova, Antti J. Karttunen, Sergey P. Tunik, Igor O. Koshevoy
Dibenzothiophene-platinated complexes: probing the effect of ancillary ligands on the photophysical performance
Dalton Transactions Issue 12, Pages 3895-3905
DOI: 10.1039/C7DT00349H

Cyclometalation of dibenzothienyl-pyridine (HPyDBT) afforded a series of platinum(II) complexes Pt(PyDBT)(L)Cl (L = DMSO, 1; P(p-C6H4-X)3 (X = H, 2; CF3, 3; OMe, 4; NPh2, 5); 1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane, 6; 2,6-dimethylphenyl isocyanide, 7). Chelating bidentate LL ligands formed cationic compounds [Pt(PyDBT)(LL)]+ (LL = 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)benzene, 8; 2,2’-bipyridine, 9; 1,10-phenanthroline, 10). Oxidation of a thienyl sulfur atom allowed for the isolation of the sulfone derivative Pt(PyDBT)(PPh3)Cl (11). The title complexes were characterized crystallographically (except 7). Investigation of their photophysical behavior revealed solid state phosphorescence with quantum yields up to 0.45 for neat powders. The ancillary ligands L show a minor influence on the emission energies of the neutral compounds, but affect dramatically the intensity of luminescence. In contrast, the cationic species with diimine ligands demonstrate a significant contribution of the LL fragments into the emissive T1 states that leads to a certain mixing of 3IL and 3LL’CT transitions and causes a substantial bathochromic shift of emission.
23 марта, дискуссионный семинар по Bryozoa, в ЦКП «Хромас»
23 марта 2017 г (четверг) в 16 часов в ресурсном центре ЦКП «Хромас» Научного парка СПбГУ состоится очередной семинар.
Тема доклада "Symbiont dependent host reproduction in the marine bryozoan Bugula neritina"
Подробнее: 22.03.2017 23 марта, дискуссионный семинар по Bryozoa, в ЦКП «Хромас»




